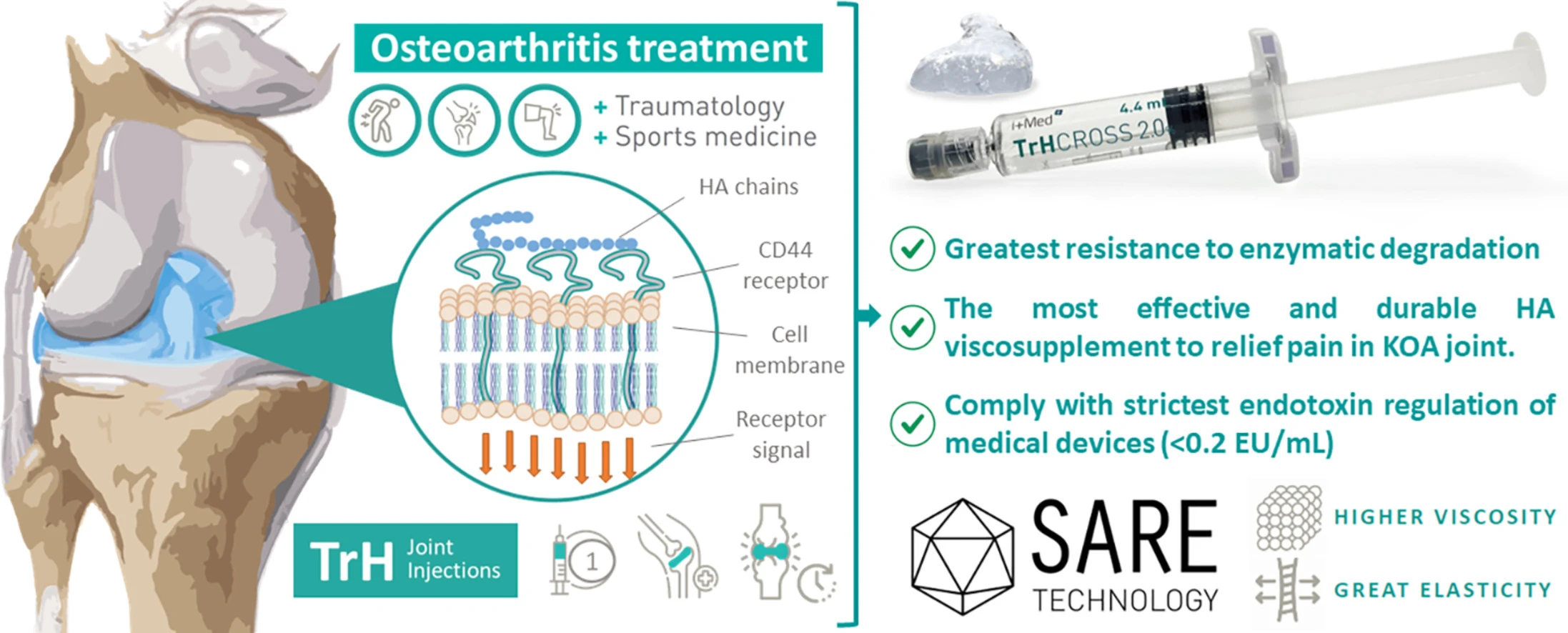
There are dozens of different hyaluronic acid injections for knee osteoarthritis, each with its own formulation and technology. Many patients and physicians ask: which one works best? In this article, we compare the main products based on independent scientific research to help you understand which factors truly determine the effectiveness and duration of the injection.
Why It’s Important to Compare Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Not all hyaluronic acid injections are the same. They differ in molecular weight, concentration, crosslinking technology, and biological stability. These factors influence how long the product remains active in the joint, how well it lubricates, and how the body responds to it.
What Determines the Effect of a Hyaluronic Acid Injection?
The molecular weight of hyaluronic acid (measured in kilodaltons or megadaltons) defines the size of its molecules. Larger molecules tend to remain in the joint longer but spread more slowly. In addition, the crosslinking technology plays a crucial role: these chemical bonds make the molecules more resistant to enzymatic breakdown, such as by hyaluronidase.
Scientific Research on Hyaluronic Acid Injections (del Olmo et al., 2023)
An independent laboratory study published in Carbohydrate Polymers Technologies and Applications (2023) evaluated four commercial hyaluronic acid products: TrHCROSS®, Durolane®, Regenflex® Bio-Plus, and Monovisc®. The researchers compared the products in terms of rheological properties (viscosity and elasticity), chemical composition, injection force, and enzymatic degradation.
Comparison of Specifications
| Product | Crosslinking Technology | % Hyaluronic Acid | Crosslinking Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| TrHCROSS® | SARE® Technology | 2.0% | 1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE) |
| Regenflex® Bio-Plus | BIORIVOLUMETRIA® | 2.5% | BDDE |
| Durolane® | NASHA® Technology | 2.0% | BDDE |
| Monovisc® | Unknown | 2.2% | Not specified |
TrHCROSS® – SARE® Crosslinking Technology
The results show that TrHCROSS® demonstrated the highest elasticity (78.7%) and the lowest tan δ value (0.27) — indicating a stable and resilient gel structure. It also showed the greatest resistance to enzymatic degradation and an ideal pH of 7.36 with osmolality close to physiological levels (305 mOsm·kg⁻¹).
Durolane® – High Molecular Weight but Lower Stability
Durolane® has a very high molecular weight (10,000 kDa) and is strongly crosslinked. While this provides a thick consistency, the study showed that its elasticity was lower (70.7%) and its pseudoplasticity higher, indicating less stable viscosity during movement. The pH was also lower (6.93), which may affect post-injection comfort.
Regenflex® Bio-Plus – Moderate Viscosity
Regenflex® Bio-Plus showed moderate elasticity (63.3%) and a tan δ of 0.58, meaning the gel is less stable under stress. Its osmolality was slightly below physiological levels (293 mOsm·kg⁻¹) but still within a safe range.
Monovisc® – Low Viscosity, Shorter Duration
Monovisc® is a non-crosslinked formulation with the lowest viscosity (η = 3.8 Pa·s) and the highest loss factor (tan δ = 1.58). This makes it easier to inject, but it also has a shorter duration of action. Its molecular weight is relatively low, and the gel shows limited elasticity (38.8%).
Molecular Weight vs. Crosslinking: What Does Research Really Show?
Many believe that a higher molecular weight automatically means a longer-lasting effect. In reality, crosslinking technology and enzymatic resistance are much stronger predictors. A well-balanced product with a moderate molecular weight and strong crosslinks often remains active longer than a heavier but less stable formulation.
| Parameter | Influence on Duration |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | Determines viscosity but not stability |
| Crosslinking Technology | Strong predictor of degradation rate and longevity |
| Elasticity (G′) | Important for resilience during movement |
| pH and Osmolality | Influence comfort and biocompatibility |
Clinical Results and Safety
According to several studies (Altman et al., 2015; Bannuru et al., 2019; Acín et al., 2025), hyaluronic acid injections can delay the need for total knee replacement by an average of two years. Crosslinked injections such as TrHCROSS® provide longer-lasting pain relief and are safe for repeated use due to their low BDDE residual content (<0.15 ppm).
Conclusion: Which Hyaluronic Acid Injection Works Best According to Research?
Based on both laboratory and clinical studies, it is not the highest molecular weight but rather the balance between viscosity, crosslinking, and stability that determines how well a hyaluronic acid injection performs.
- High molecular weight ≠ automatically longer duration
- Crosslinked HA with strong SARE® technology remains active longer
- TrHCROSS® showed the highest enzymatic resistance and elasticity
- Low BDDE residue and physiological pH ensure excellent tolerability
Conclusion: According to independent laboratory research (del Olmo et al., 2023), TrHCROSS® provides the most stable and durable viscosupplementation for knee osteoarthritis—without compromising safety or comfort.
Considering a Hyaluronic Acid Injection? Share This Comparison with Your Physician
Has your doctor or orthopedist recommended a hyaluronic acid injection? Or are you researching the available options yourself? Feel free to use this article as a reference during your next consultation. An informed decision—made in collaboration with your physician—helps achieve the best possible treatment outcome.
Is your doctor not listed among our treatment locations?
You can also have the injection administered by your own physician. Would you like to learn more about TrHCROSS® or have additional questions? Contact us—we’ll gladly provide you with further medical information or practical guidance.